What Is Economics?
Understanding economics goes beyond simply comprehending the meaning of the word. It requires a deeper understanding of its fundamental concepts. So before we move on to deeper discussions, let’s talk about them first.
Economy
One such concept is the economy. Granted, it is a word we hear nearly every day. But do we really know what it means?
In layman’s terms, the economy is an organized system that produces and provides a society with the goods and services it needs to exist and function. It increases in size together with the society it provides for.

Naturally, we can measure the value of all the goods and services the economy produces. Hence the term gross domestic product (GDP) — it is the measure of the size of the economy.
Types of Economic Systems
When we want to define an economic system, we can do so by looking at:
- the way goods and services are produced;
- the way goods and services are allocated within society.
Based on that, and looking back at societies that have existed in history, we see:
- Primitive agrarian societies, which were self-sufficient and with virtually no concept of private property. In them, people provided only for their own or the needs of their own family or tribe. There was little to no division of labor, and trade was based on a reciprocal exchange between families or tribes.
- Feudalism and slavery, which were both founded on class-based production. While slavery implied an entirely disenfranchised workforce trapped in forced labor, feudalism offered a sort of a trade-off — safety and security in return for hard labor. In both instances, the products were usually intended for the higher class’ personal use.
- Capitalism, which heavily relies on the concept of private property and market. In it, business owners make a profit through the production goods. They are the sole owners of the entire business process and the final product. The labor force works in return for wages and can claim no rights over the product.
- Socialism, which relies heavily on an equal distribution of work and profit. In it, workers collectively own a business, work in production, and share the profit. The market is a way to distribute goods and services.
- Communism negates the existence of private property altogether. As a result, all members of a society own all the tools used in production. The market is virtually non-existent, as a central system is in charge of labor and distribution organization.
Scarcity
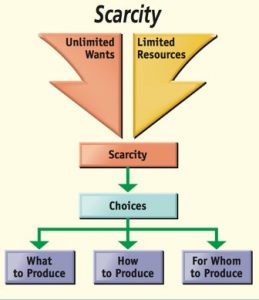
Put simply, scarcity is an obvious disbalance between the limited resources on the one hand and the unlimited wants and needs on the other. It is another fundamental concept of economics, and we can apply it both to individuals and entire societies.
Namely, an individual relies on resources such as time, money, and skills. Societies, on the other hand, rely on resources like capital, labor force, technology, and natural resources. Obviously, the resources are not infinite, and we need to manage them based on what we want and need.
Macro and Microeconomics
We study economy from two basic standpoints — that of macroeconomics and microeconomics. They are narrowly connected. Therefore, studying them gives valuable insight into how a society’s economy functions on both the micro and the macro levels.
Macroeconomics
Experts in this field study economy on both the national and international levels. They examine a nation’s GDP and the way the system allocates resources to the members of the society. Furthermore, they study international trade, as well as the nation’s fiscal and monetary policy. Finally, they analyze the level of inflation, interest rates, and the unemployment rate.

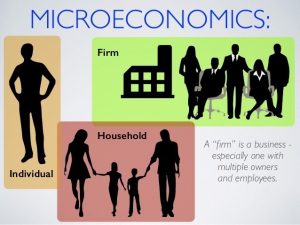
Microeconomics
This field of study focuses on analyzing aspects of human behavior that directly influence fluctuations in prices, supply, and demand. Experts make attempts at explaining how and why certain goods have an influence on individuals’ financial decisions, as well as the ways in which individuals coordinate and cooperate among themselves.

0 Comment